The Windows Credential Manager can be used to securely store user id’s and passwords, so they can be referenced in code without being written in your code when automating a sign in process. This opens up the door to access secure objects, such as a Microsoft SQL Server databases, as shown below. To see how to do this on a Mac, check this out.
Add Credentials to Windows Credential Manager
The Credential Manager app is native to Windows and can be found by searching from the start menu. Once open, navigate to the “Windows Credential” menu. This will display existing credentials and allow credentials to be added by selecting “Add a Windows Credential”.
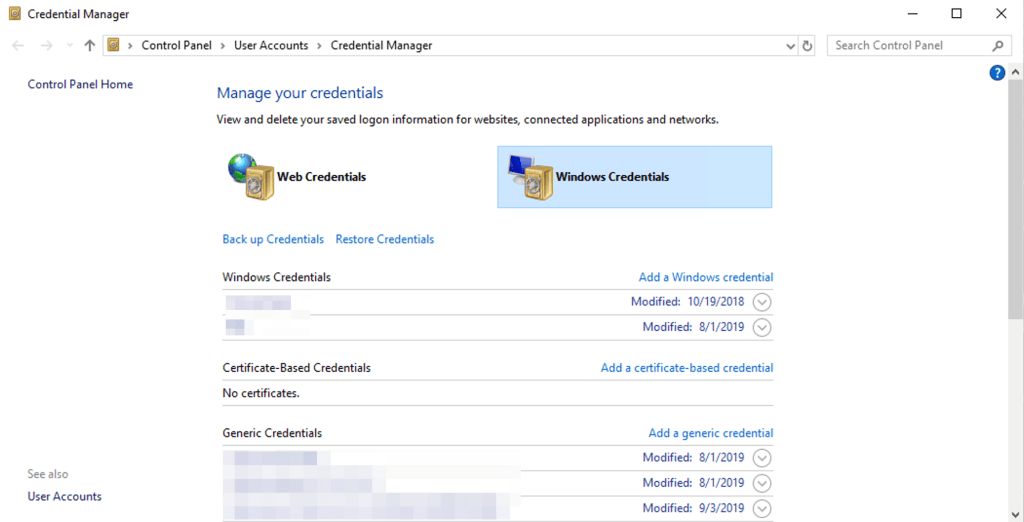
In the Add a Windows Credential menu, enter the easy to understand name for what the credentials connect to, in this case SQL. The username and password fields are what would would be entered to connect to the SQL instance.
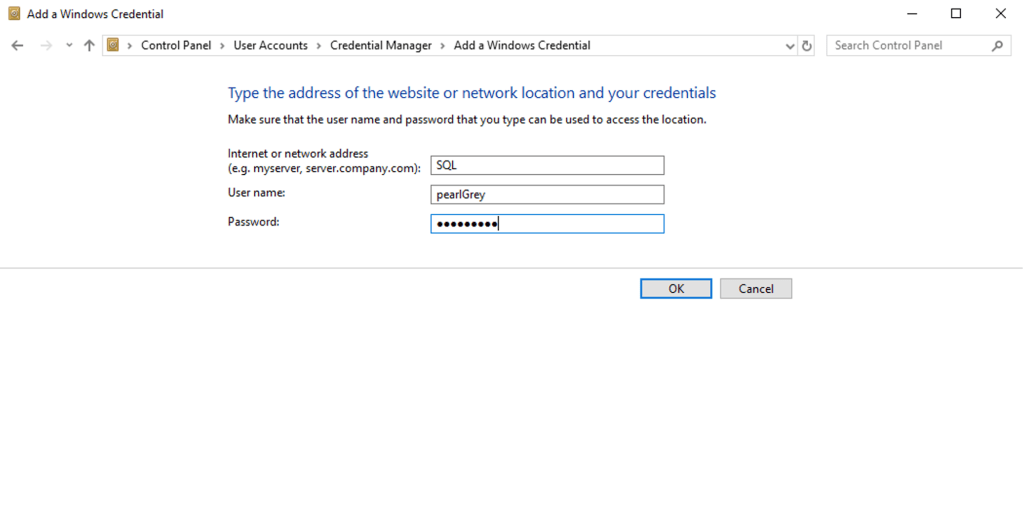
After selection “OK” the credential will display and is ready to be referenced in an R script.
Connect to SQL in R
Now that the credentials have be added to the manager, functions can be written in R to automate connecting to SQL, using the sqlPlug() and sqlGrab() functions and the Windows SQL driver. In the below example, the Server is referenced through the Credential Manager as well, but this can also be referenced as a character string. The user id and password are referenced using the “SQL” entry created above.
library("DBI")
library("odbc")
library("svDialogs")
library("dplyr")
library("getPass")
library("keyring")
sqlPlug <- function() {
dbConnect(odbc::odbc(),
Driver = "SQL Server"
# Driver = "ODBC Driver 13 for SQL Server", # mac driver
, Server = key_list('SQLServerName')[1,2] # pulls from Win Cred Manager
, Database = "databaseName"
, UID = key_list("SQL")[1,2] # pulls from Win Cred Manager
, PWD = keyring::key_get("SQL", key_list("SQL")[1,2]) # pulls from Win Cred Manager
)
}
sqlGrab <- function(con, queryText) {
dbSendQuery(con, queryText) %>% dbFetch()
}
con = sqlPlug()
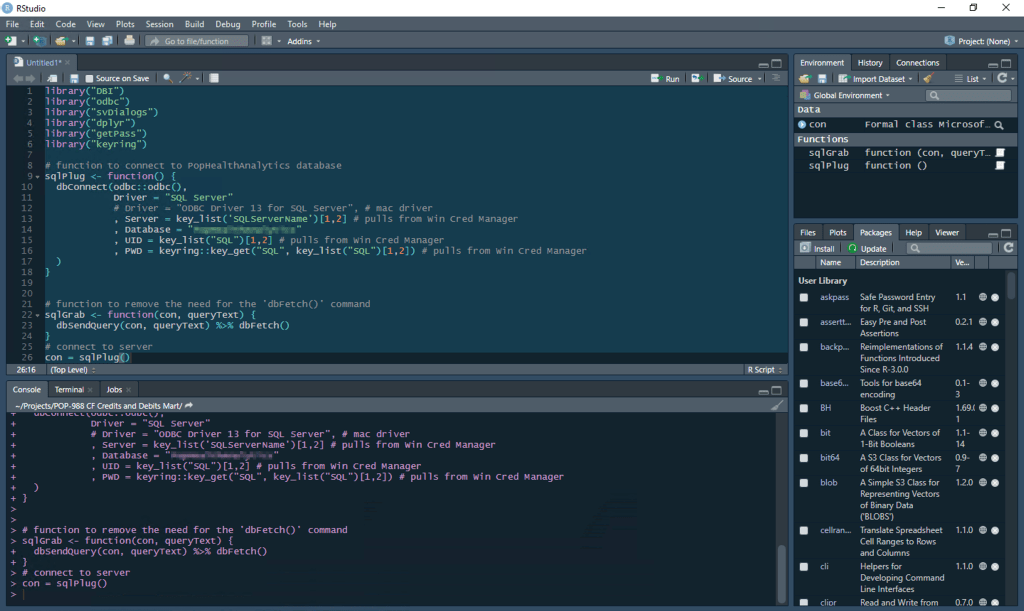
Using the read_file() function from the readr package, a prewritten query can be called to execute and return number of drinks sold for all the branches of a chain restaurant in a given city. The sqlGrab() function will execute the query text and save the results as a data frame.
queryText = readr::read_file(paste(Sys.getenv('USERPROFILE'), '/Documents/rop/credentialManagerWin/sqlQuery.sql', sep = ''))
sqlExport = sqlGrab(con, queryText)
Once the data is in R, the possibilities are endless! This restaurant example in later posts to show how to other data from a Google Sheets file (or other sources) and compare both sources by programmatically generating a pivot table.